Automotive internal high voltage cables are critical components in modern vehicles, especially electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid systems. These cables carry high voltage electricity between the battery, inverter, motor, and other electrical systems. Due to the high power levels, any fault or improper handling can pose significant safety risks, including electric shock, fire hazards, and system malfunctions. Understanding their construction, insulation, and safety requirements is essential for manufacturers, technicians, and vehicle owners.
High voltage cables differ from standard automotive wiring in terms of voltage rating, insulation thickness, and safety standards. They must withstand thermal stress, mechanical wear, and chemical exposure while ensuring reliable performance under dynamic vehicle conditions.
Construction and Materials of High Voltage Cables
High voltage automotive cables are typically composed of a conductive core, insulating layers, shielding, and protective outer jackets. The conductive core is usually made from copper or aluminum due to their excellent electrical conductivity. The insulation is made from high-quality polymers such as XLPE (cross-linked polyethylene), ETFE, or silicone, providing dielectric strength and heat resistance.
Some cables include additional layers for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding to prevent signal distortion in sensitive automotive electronics. The outer protective jacket protects the cable from mechanical damage, chemical exposure, and environmental conditions such as moisture and temperature fluctuations.
Voltage Ratings and System Requirements
Automotive internal high voltage cables are rated based on the maximum voltage they can safely carry. EVs typically use systems ranging from 200V to 800V, requiring cables with high dielectric strength. Cable ratings must comply with international standards such as ISO 6722-2 for high voltage automotive applications.
Using a cable with insufficient voltage rating can lead to insulation breakdown, arcing, and potentially catastrophic failures. Therefore, selecting cables compatible with the vehicle’s voltage requirements and environmental conditions is critical.
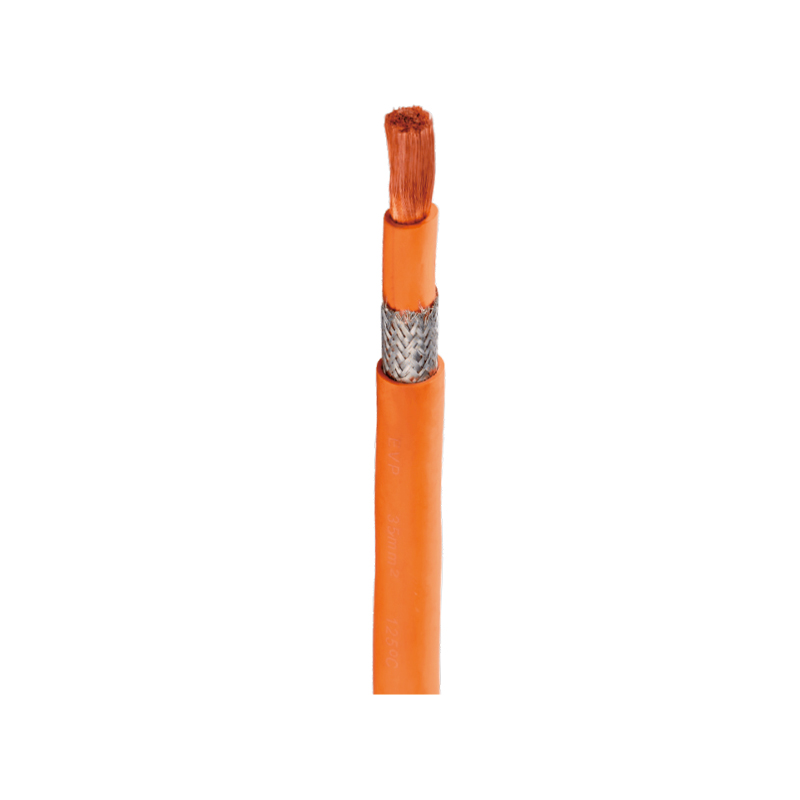

Thermal Considerations and Heat Management
High voltage cables generate heat due to electrical resistance. Excessive heat can degrade insulation and reduce cable lifespan. Proper heat management involves selecting cables with appropriate current-carrying capacity, proper routing to avoid hot zones, and ventilation or cooling strategies in battery compartments.
Cables must also be tested for thermal cycling, as repeated heating and cooling can cause expansion and contraction, potentially leading to cracks in insulation or mechanical fatigue.
Mechanical Stress and Vibration Resistance
Automotive cables are exposed to constant vibration, bending, and movement. High voltage cables must be designed to withstand mechanical stress without compromising insulation. Reinforced sheaths, flexible cores, and strain relief components help ensure longevity.
Poor mechanical protection can lead to abrasion, insulation failure, and eventual short circuits, which are particularly dangerous at high voltages.
Insulation and Safety Standards
Insulation is the primary safety barrier in high voltage cables. It must resist breakdown under high voltage, temperature extremes, and exposure to chemicals such as oils and coolants. Compliance with safety standards ensures reliability and minimizes risk. Common standards include ISO 6722-2, SAE J1128, and LV 214 for automotive high voltage wiring.
Insulation testing typically involves dielectric withstand tests, partial discharge testing, and mechanical stress testing to confirm that the cable can safely operate under real-world conditions.
Routing and Installation Best Practices
Proper installation is crucial for high voltage safety. Cables should be routed away from sharp edges, moving parts, and heat sources. Clamps and guides must secure cables to prevent vibration-induced damage.
- Avoid tight bends that exceed the cable’s minimum bending radius.
- Maintain separation between high voltage cables and low voltage control wiring to prevent interference.
- Ensure proper grounding and shielding to reduce EMI risks.
Maintenance and Inspection Guidelines
Regular inspection of high voltage cables is essential to detect wear, insulation degradation, or loose connections. Maintenance procedures include visual inspection, insulation resistance testing, and ensuring connectors are properly torqued.
Damaged cables must be replaced immediately by trained personnel using proper protective equipment to prevent electric shock or fire hazards.
Emergency Handling and Safety Precautions
Working with high voltage automotive cables requires strict safety precautions. Always disconnect the battery and isolate high voltage systems before handling cables. Use insulated tools, gloves, and protective gear. Follow manufacturer guidelines and safety protocols to minimize the risk of electric shock.
Emergency training for technicians and vehicle operators ensures that high voltage components are managed safely during accidents or maintenance procedures.
Conclusion: Ensuring Safety and Reliability
Automotive internal high voltage cables are critical for modern vehicles, particularly EVs and hybrids. Proper design, insulation, routing, and maintenance are essential to ensure safety, prevent hazards, and maintain reliable vehicle performance. Adhering to safety standards and best practices minimizes risks and enhances the longevity of these high voltage systems.
Understanding construction, voltage ratings, thermal and mechanical considerations, and proper installation ensures that automotive high voltage cables operate safely and efficiently under all conditions.



 English
English عربى
عربى Español
Español